Human aging is a universal natural law. “Biochemistry and Cell Biology of Aging” summarizes decades of aging research and attributes aging to oxidative damage and decline in NAD+ levels.
It can be seen that NAD+ plays a vital role in organisms, and it is closely related to infectious diseases and diseases.
NAD+ is called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, or coenzyme I for short. It is widely involved in a variety of basic physiological activities within the organism, thereby affecting energy recovery, resistance to oxidative damage, DNA repair, regulating genes and genomes that control aging in cells, weakening or even shutting down some aging genes, thereby effectively delaying the progression of the queue. Below, let’s take a comprehensive look at:
1.The importance of NAD+
As one of the most important metabolites in the human body, NAD+ has been in a steady state consisting of biological production, consumption, circulation and degradation for a long time.
Starting from the 30s, the NAD+ level in the human body will show a downward trend as people age. The decrease in NAD+ content in cells will in turn lead to a decrease in DNA repair ability, accelerate the accumulation of DNA damage, and then lead to the destruction of NAD+ The content further decreases, forming a vicious cycle of faster and faster aging.
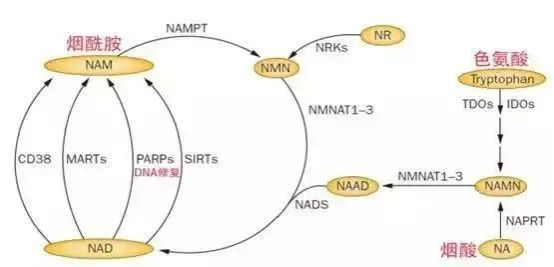
We say that NAD+ is involved in DNA repair mainly because it is a substrate of the PARP family. With NAD+, PARP can play its corresponding role. On the other hand, PARP is also one of the main “consumers” of NAD+ in cells. The NAD+ used up by PARP turns into nicotinamide NAM, and then flows into the rescue pathway, and NAD+ is synthesized again with the help of NAMPT, NMNAT and other enzymes. When cells are under stress (including DNA repair processes), large amounts of NAD+ are synthesized through the salvage pathway to maintain a balance between supply and demand.
NAD+ participates in DNA repair as a Sirtuins substrate
Sirtuins are a family of protein deacetylase consisting of 7 members (SIRT1-SIRT7). SIRT1, SIRT6, and SIRT7 exist in the nucleus, SIRT2 plays a role in the cytoplasm, and SIRT3, SIRT4, and SIRT5 are mitochondrial proteins. Some Sirtuins (especially SIRT1 and SIRT6) play important roles in DNA repair and cellular metabolism after DNA damage.
3.NAD+ metabolism and physiological functions
01. Maintain redox homeostasis
Maintaining the balance of intracellular oxidants and antioxidants is the key for cells to maintain normal physiological functions. However, adverse stimuli such as pollution, nutritional changes and infection can disrupt this balance and cause damage to biological macromolecules such as DNA and proteins. Supplementing NAD+ can play an oxidative protective role by increasing the levels and activities of glutathione and a series of antioxidant enzymes.
02. Maintain genome stability
Lack of NAD+ will cause obstacles to DNA damage repair, causing a large amount of DNA damage to accumulate, and supplementing NAD+ can help DNA repair.
03. Regulate immunity and inflammation levels
In addition to NAD+ itself being able to slow down excessive inflammation levels by improving lysosomal function, the NAMPT enzyme necessary in its metabolism is also an important part of regulating immunity. Supplementing NAD+ helps regulate immunity and inflammation.
Mobile Phone: 86 18691558819
Irene@xahealthway.com
www.xahealthway.com
https://healthway.en.alibaba.com/
Wechat: 18691558819
WhatsApp: 86 18691558819
Post time: Dec-26-2023